The “People Also Search For” (PASF) boxes that appear in Google search results are intended to help users discover similar topics and broaden the scope of their search. It can be especially helpful when a user’s search query isn’t clear or isn’t very specific.
Google wants to make it easier for users to find the information they are looking for by showing that people also search for keywords. You can gain a better understanding of a topic by learning about related keywords that other people have also searched for.
You can discover what your visitors are looking for during their search journey on Google. And “People also search for” phrases helps to develop content that will keep them engaged. Given that these keywords are directly originating from Google, this is a gold mine for SEO and PPC practitioners.
In this article, we’ll discuss about :
But how does PASF feature affect SEO and PPC, you ask? It does and to a great extent!
Google’s SERP has changed dramatically over the years. Depending on the type of question asked, Google shows different types of search results and snippets to users.
Google needs to make sure that its search results only show the most trustworthy, relevant, and high quality webpages, if it wants people to keep using it as their favorite search engine. As a result, it is constantly experimenting with new things on its Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs).
Google’s search result page is far more dynamic than that of competitors such as Bing. Google focuses more on paid ads, featured snippets, and sections like “People also search for “, “People also ask “, “Related searches”. That’s why the path to rank on organic search has also changed.
People also search for (PASF), a frequently overlooked but critical component of Google’s search results page. Not familiar with it? No issue!
In this blog, we’ll explain how PASF works, why it’s important, and how you can use it to improve the SEO and PPC performance of your website. Also, how to find and rank for these keywords.
Let’s get started!
What is People also search for box in Google SERP?
People also search for (PASF) aims to assist users in finding the information they are looking for. While the PASF box is not a new entry to Google’s SERP, it has undergone some changes to become what it is today.
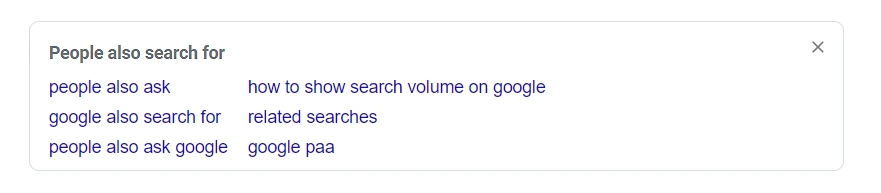
People also search for or PASF is a dynamic entry. It is not always visible on all searches, and is case-sensitive.
Confused? Don’t be that way!
Let’s go over how Google’s People also search for feature works, when they appear. And how you can rank for these keywords.
How do you see what people also searched for on Google?
Being a dynamic entry, People also search for box is not initially displayed. It only appears after you have clicked on an initial organic result, and then returned back to the SERP by hitting the browser back button.
Here are the steps to see people also search for on Google:
- Search for something
- Click on any search results
- Click the back button of your browser
- People also search for shows up under the search result you originally clicked on
In other words, Google assumes that you didn’t find what you were looking for on that site and gives you more ideas.
However, People also search for results differ from regular SERP results. The PASF box is URL focused. This means it displays snippets from the website you just visited. So what people also searched for appears just beneath it.
Typically, mobile search results provide even more PASF options. According to market research, nearly 80% of mobile SERPs and nearly 60% of desktop SERPs display a “People also search for” box. These percentages indicate that this is a golden opportunity for SEO and PPC professionals.
Case Study: Here, we conducted a search for “how can an invention be protected”. Here is the search query: https://www.google.com/search?q=how+can+an+invention+be+protected and following is the SERP:
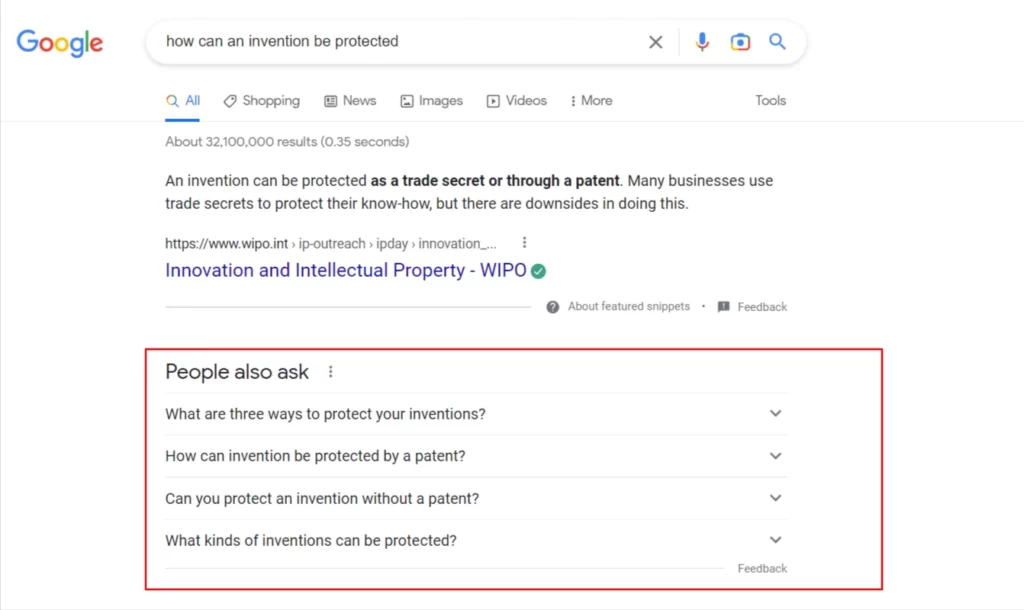
Next, let’s visit the 2nd search result, Wipo.int, and then return to Google (it works both within the same tab and when you open it in a new tab and close it).
When we return, an additional section drops down from that result. The keywords that people also search for are related to the Wipro.int website and not to the original search phrase we typed.
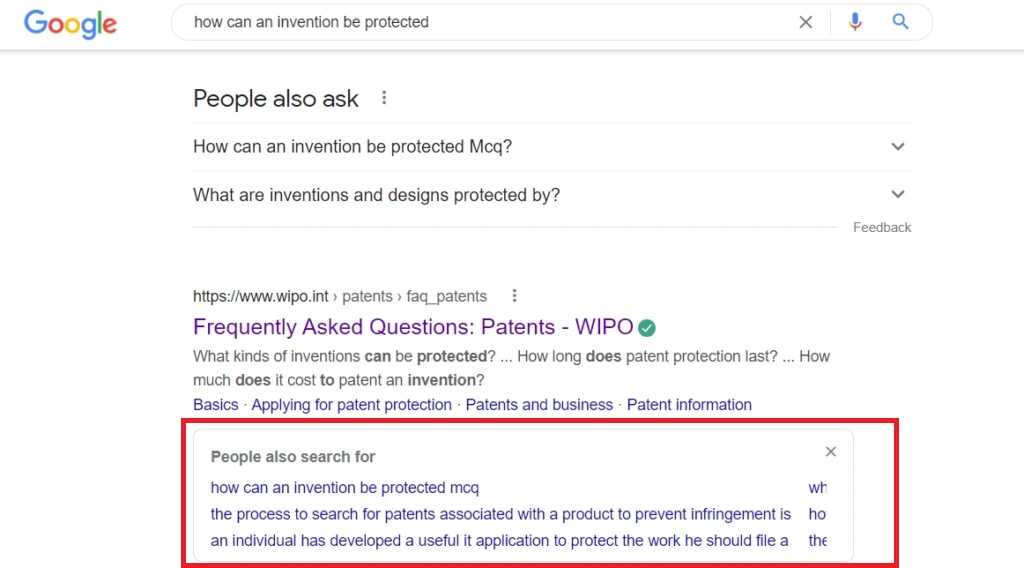
On a desktop, you can also access the “People also search for” section from the search box itself, another new addition. So, how does this differ from the way people also search for sections that appear along the URL visited?
Let’s search for “Marie Curie.”
Now, clicking on the search box again expands the suggestion list to include another “People also ask” (PAA) and “People also search for” (PASF) section. The PASF results here are centered on the search string and not on any URL visited. Thus, they are much more generalized.
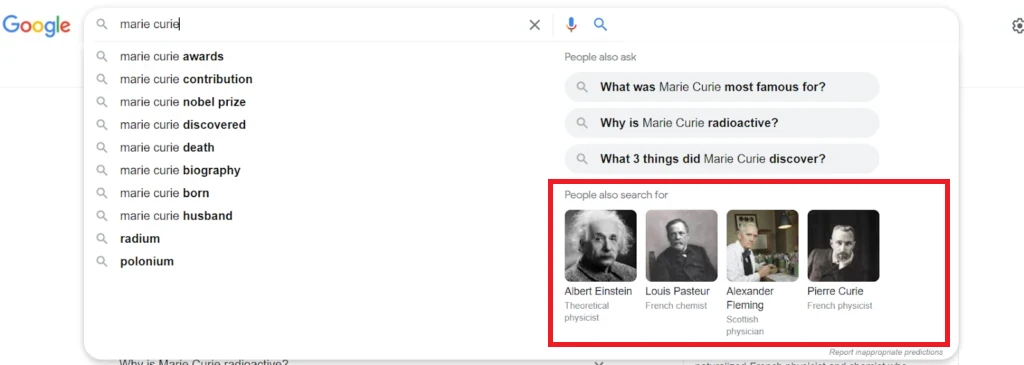
Again, this is not a new search feature but simply an additional placement. You might be familiar with the right hand snippet that appears when one searches for specific items. Here too, we see a “People also search for” section at the bottom. The same is simply reiterated within the search box.
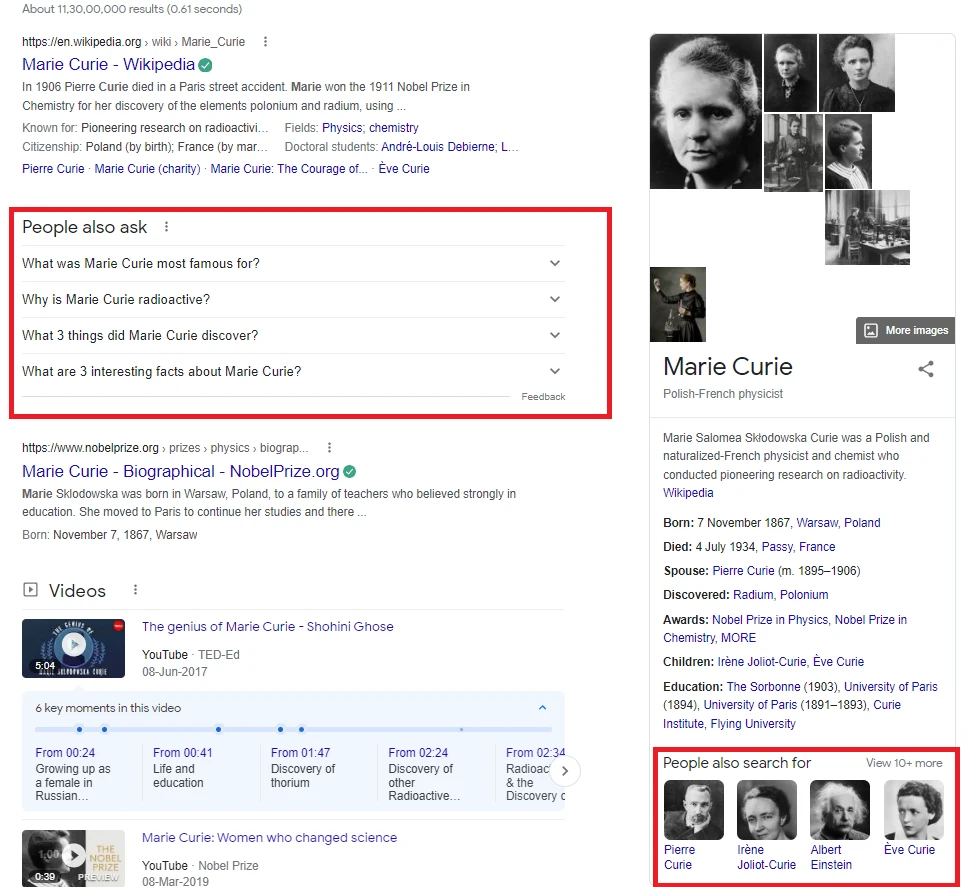
However, the PASF along the search box does not appear for every term. For our earlier search term, there is no further PASF section along with the search box.
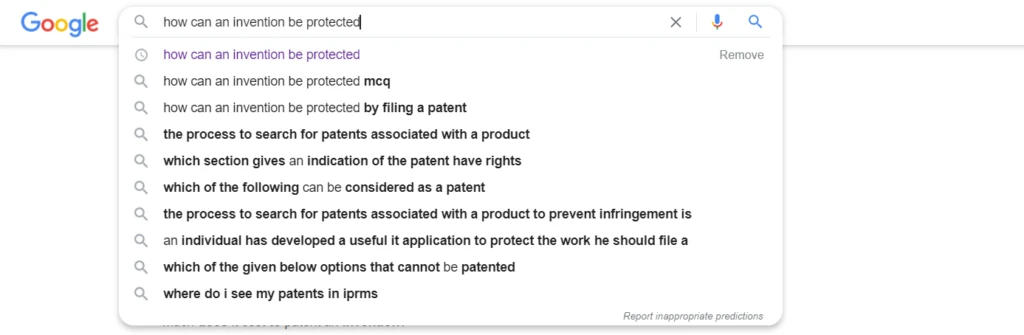
Google’s “People also search for” feature works great for music, movies, books, and other similar recommendations. Here too, we get a static People also look for sections beneath streaming and purchasing recommendations.
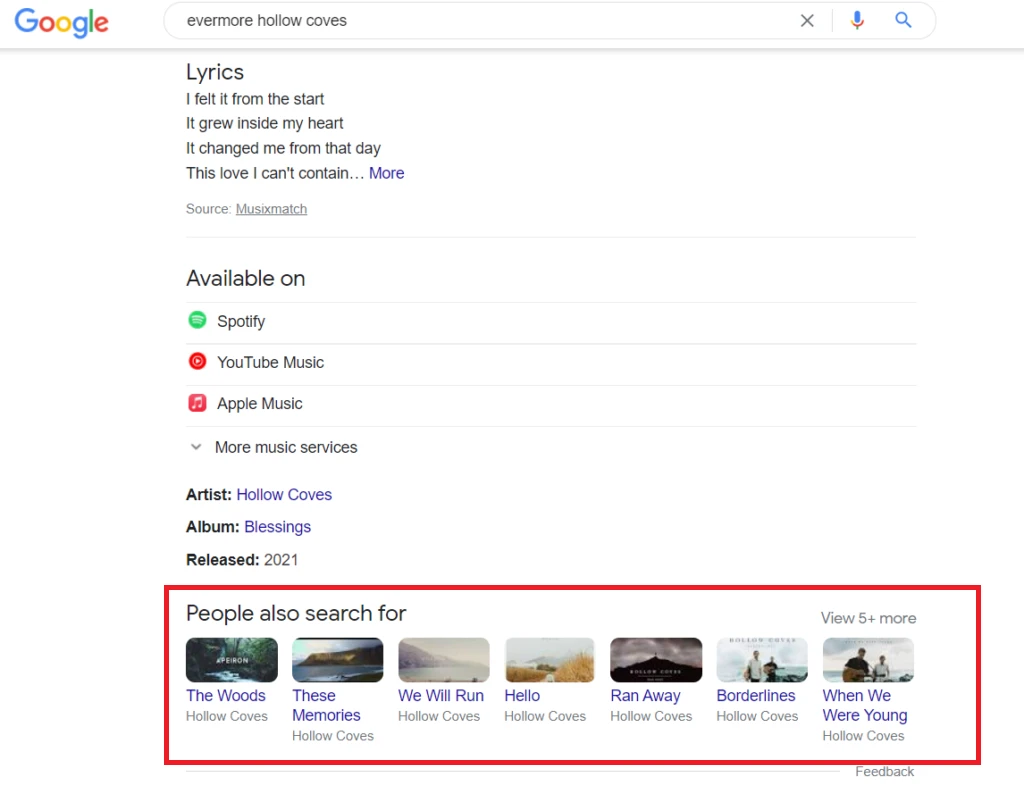
People also search for, which is a gold mine for anyone who knows how to use these terms to their advantage. You essentially get data directly from Google based on their understanding of search intent and patterns.
How People also search for (PASF) works, and what you should know?
Before getting into how you can use the PASF results to your SEO, PPC, and content writing advantage, let’s understand the ins and outs of what triggers PASF.
- Trigger: The trigger that People also search for is visiting and closing a search result tab. The PASF box, on the other hand, appears for all search results, both organic and paid. Below you can see the People also search for box being positioned for the top result, which is a paid ad.
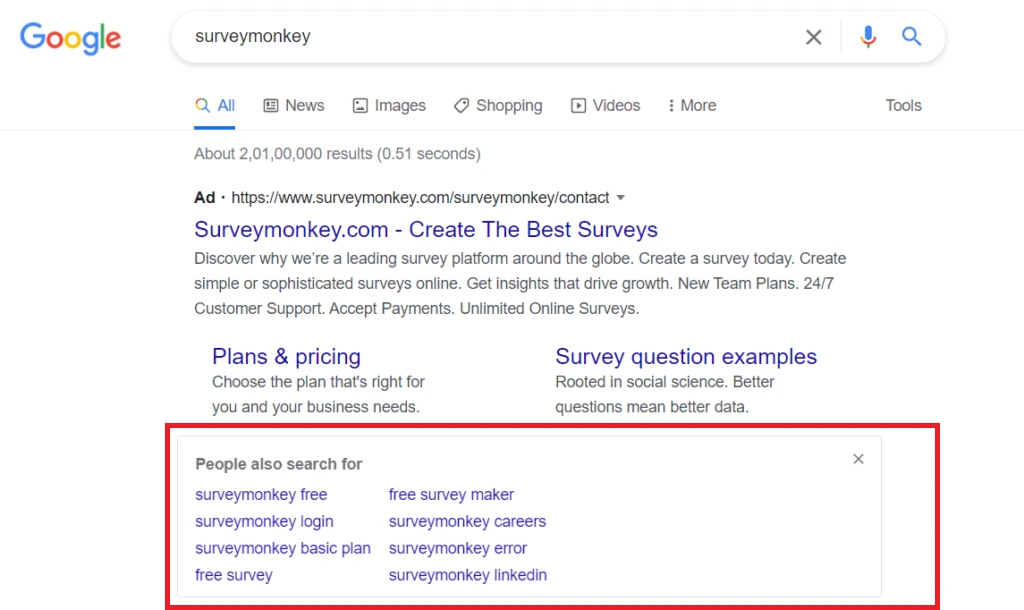
If you click on a Featured Snippet result or a People also ask result and return, the PASF box is not activated. The same goes for the Related Searches section.
- Position of the PASF box: People also search for is a dynamic entry which means it drops down from the URL you visited and closed. As such, it changes position depending on your search pattern. Google will keep offering PASF boxes for each search result that you visit and close. In the screenshot below we have 3 on the same page. The overlap between these can offer some interesting SEO insights. You can use the cross button to close these boxes at any time.
- Mobile vs. desktop: On desktop, people also search for, which returns six results. On mobile, it returns four results. If you are using a browser other than Chrome, like Safari or Firefox, dynamic content like the PASF box may not be displayed at all. Static content like featured snippets and the People also ask section are not affected.
Timeline of Google People also search for feature updates
| 2012 | The “People Also Search For” section made its debut in the form of image thumbnails. The feature is still present today as we saw while searching the term “Marie Curie”. As Google started working with knowledge graphs, the PASF box evolved as something that directed people towards related topics. |
| 2020 | Google started experimenting with the PAA and PASF features. Originally, it featured the PAA box in the form of related questions. |
| 2021 | The final People also search for box as we see today was rolled out and is currently running on both desktop and mobile versions. |
Other related features by Google
While People also search for is a great tool to understand user search intent, the Google search result page has many different segments that offer different types of data.
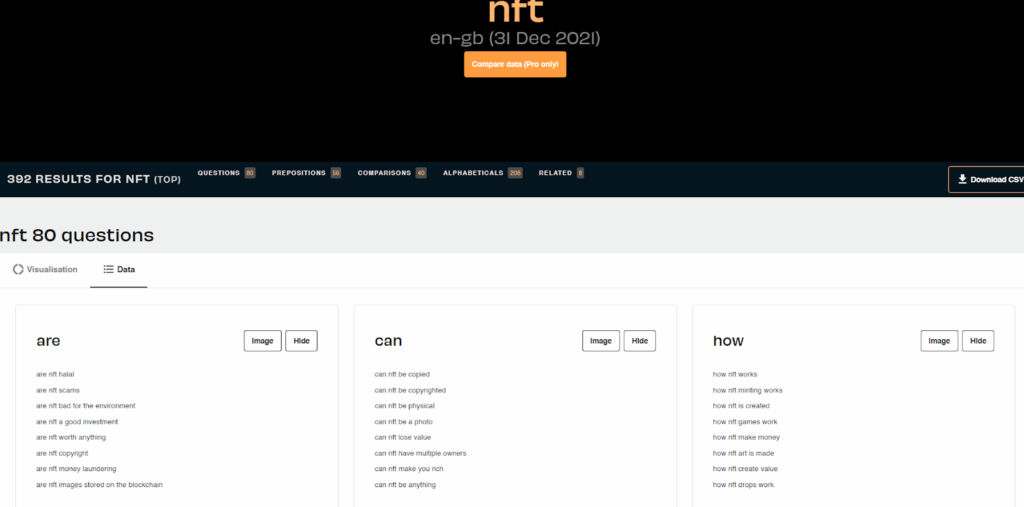
To better understand how to read their data, let’s conduct a simple Google search for “NFT”.
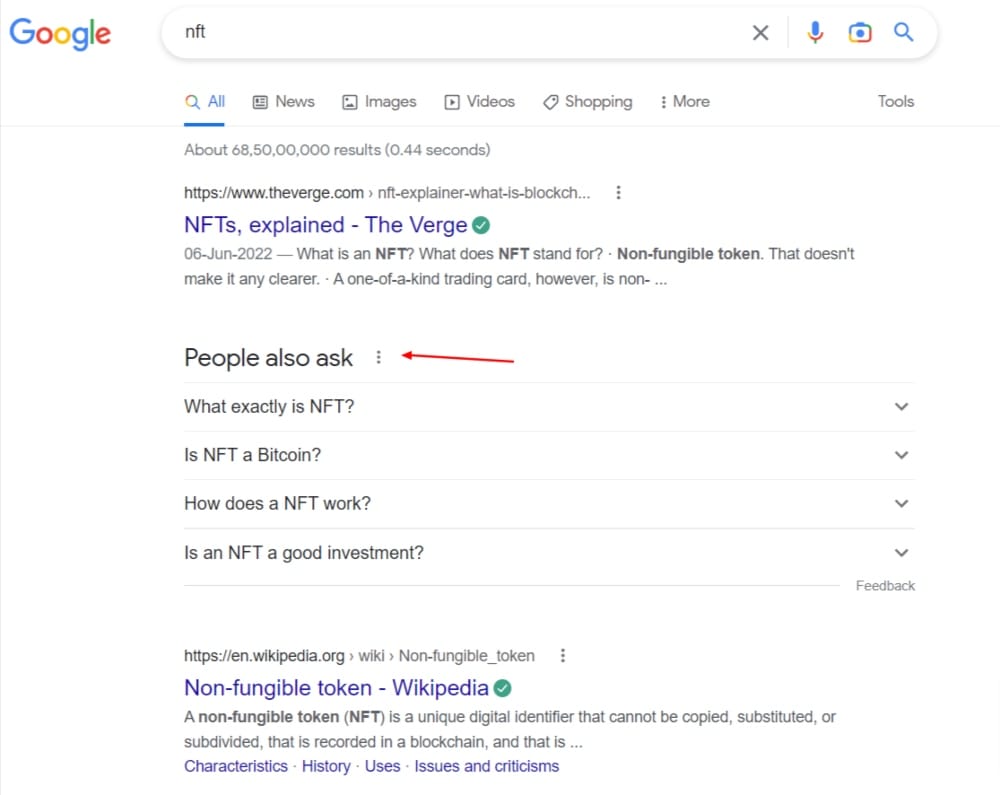
1. Search Results
This refers to the regular search results that appear on a page. Search results appear based on the presence of your search term or related terms on that page. For example, for NFT, search results include the primary term – NFT, and related secondary term – NFTs. You can see this by clicking on the 3 dots next to a search result and accessing the “About this result” section.
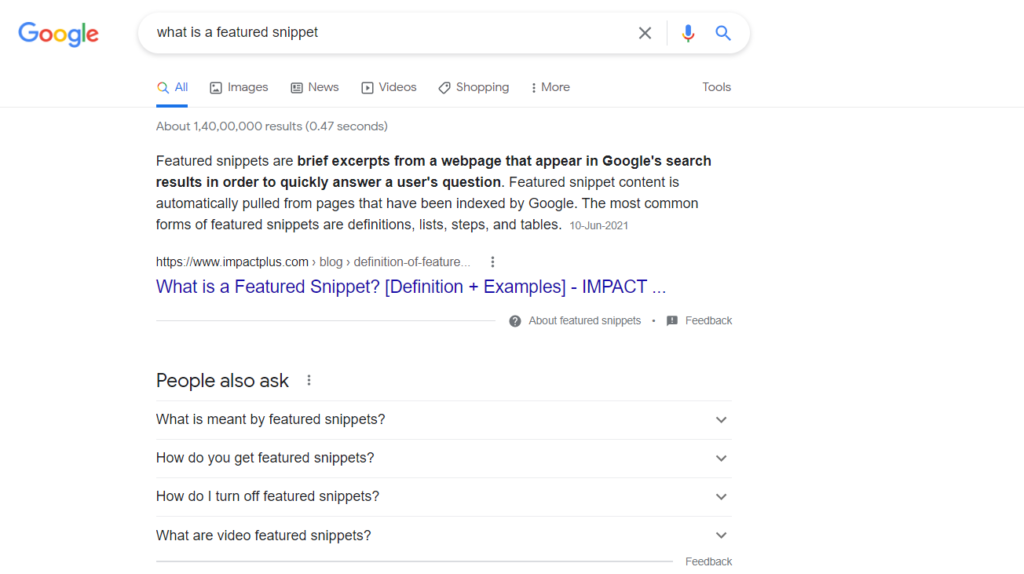
2. Featured Snippets
These are displayed in two ways. The top result can either be a snippet in itself as seen here.
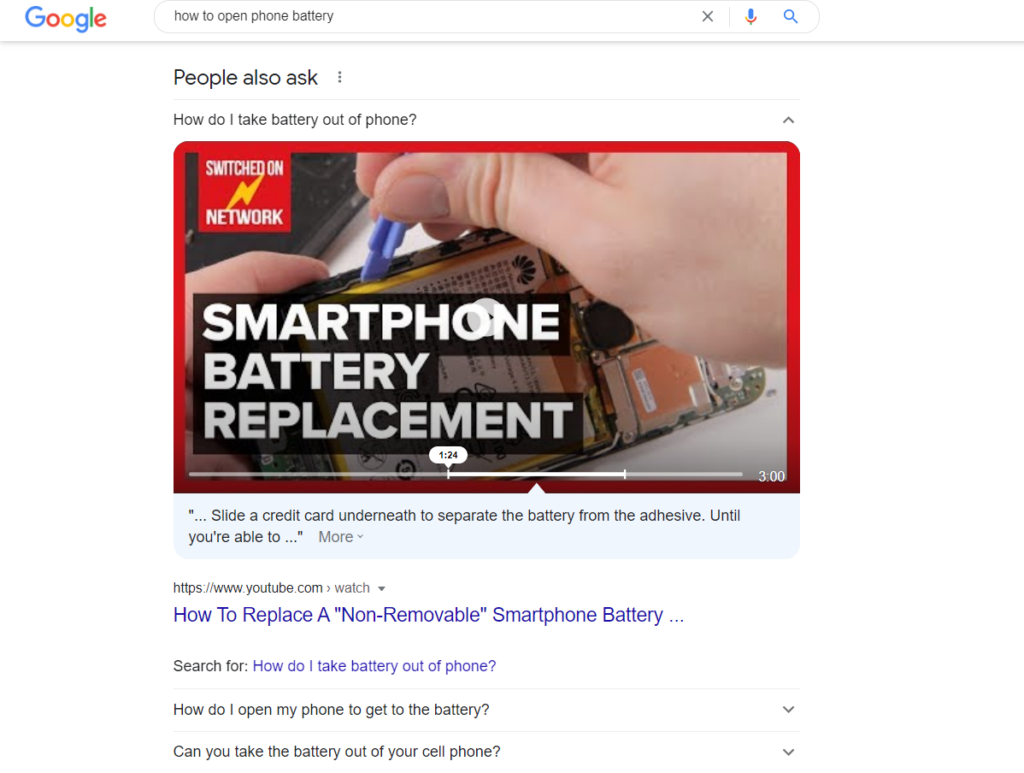
You can see further snippets when you expand on the People Also Ask section as seen next.
3. People Also Ask Section
The People also ask section differs from the People also search for section in that it offers questions and not keywords.
And it also offers multiple result types. For search terms that are questions, the People also ask section (PAA) might include video results with part of the video highlighted. In the search result here, clicking on the first PAA result opens up a video snippet.
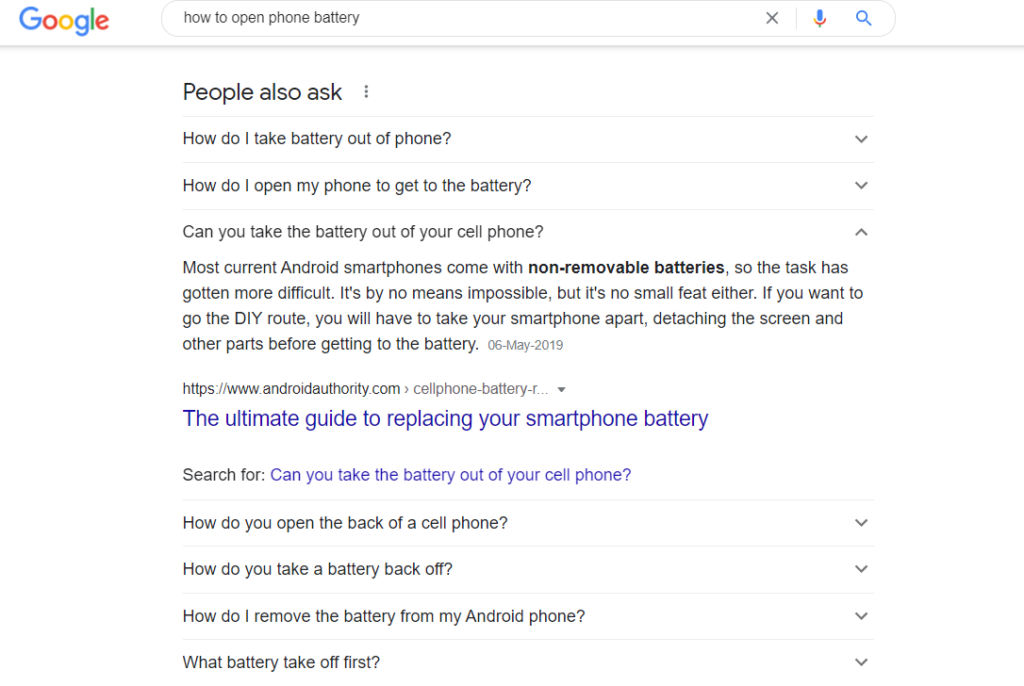
The position of the PAA section is also dynamic. It may appear at different positions however, it is always present and does not appear later like the PASF box. Also, unlike the PASF section, PAA offers a featured snippet of text as seen below:
4. Related Searches Section
Present at the end of the page, the Related Searches Section aims to provide other related search terms that you can look at. For example, if you look up a musician, the Related Searches Section might suggest other such musicians, whereas the PASF section would look at the same musician’s discography. On the whole, the Related Searches section drives you away from your original topic to similar topics.
How to make use of Google People also search for (PASF) keywords?
Here are a few suggestions to use People also search for keywords to satisfy user intent and get higher rankings in search results
- PASF can be used for keyword research.
- Use PASF to generate content ideas.
- Use PASF to create an outstanding outline.
- Use PASF to optimize your content.
- PASF can be used as FAQs.
- PASF can help you improve your on-page SEO.
- Use PASF for long-form content.
- Use PASF for interlinks and backlinks.
- Use PASF for creating ad copy.
Simply follow the steps below to leverage Google’s “People also search for” keywords:
Because there are often so many options, it can be hard to figure out which keywords are best for a certain topic or business. Keyword trends can change quickly, which makes it hard to stay relevant and make sure your content is optimized for the best keywords.
It is critical to ensure that content is not only keyword optimized, but also useful and interesting to users. It can be difficult to strike the right balance between keyword optimization and user experience.
1. Understanding the user intent behind searches
Simply knowing that “NFT” has a high search volume does not really help us figure out what it is that users are looking for. However, once we look at the PASF results for the same such as: how to create an nft, nft price and nft marketplace, we get a better idea of what users are interested in at the moment.
Once we combine this with the People also ask results: how can I buy NFTs, and are NFT a good investment? – the intent becomes much clearer. Thus, utilizing the People also search for results can help you identify the user intent behind searches as well as identify what user search patterns are.
What do we mean by search patterns? Simply, how users move through topics to find what they are looking for. People also search for is meant to answer the user’s next query or search intent.
Here’s a search for Brad Pitt.
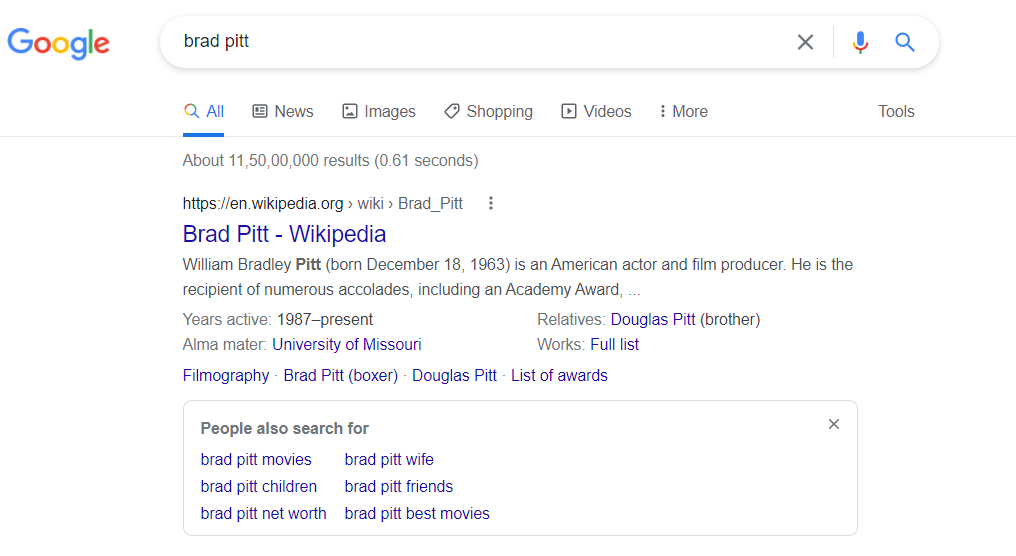
The PASF tells us more about what people usually look for next and answers them. That’s how they were designed, as per Google’s former senior vice president Amit Singhal. Singhal rewrote the original Google algorithm devised by its founder Larry Page.
Thus, the suggestions are offered based on Google’s own algorithm and data collection. In other words, you get data without investing in your own tool for analyzing the same!
How to implement It?
- Create relevant content by studying PASF results: Try to find out what it is that the customer is looking for. In other words – identify the search intent for your keyword. Once done, try to create content surrounding that intent. Doing this will also help you realize if there needs to be any restructuring in your webpage.
- Include major seed terms in your content: PASF terms often repeat for multiple websites. PAA results can be the same for more than one search term. Identify these seed terms that are repeated using excel – these are the terms your content must have! By creating organic content that focuses not only on the search term but the PASF terms, people might revisit your page as their next-in-line query comes up. It is a way of generating secondary traffic.
2. Identify popular search engine categories
Data structuring is extremely important for search engines to be able to find their way through your website. Hence, anything that helps them identify items including tags, metadata, and other types of categorization can go a long way towards improving your SEO score.
How to implement It?
Rather than looking at individual products, you might also want to categorize them as per the popular categories.
Think of it in this way: you might be selling a “Philips HD2582/00 Pop-up Toaster”. But people are more likely to search for something like ”Philips toaster” or “Pop-up toaster”.
Once you’ve recognized the category as Toaster (or Kitchen Appliances), you can then move ahead and look at the common FAQs and searched questions under these categories.
- Add an FAQ Page: FAQ pages are a great way to organically include user search terms and topics into your content. A lot of the ‘People Also Ask’ for results come up in the way of commonly asked questions. There are many existing templates available in the form of funnels that slowly draw in users. Adding an FAQ scheme as a specialized markup code also allows search engines to know that you have one and sift through it. Thus, we get one more point for SEO!
- Include 5 W’s: The 5 W’s include who, what, when, where, and why. One look at the PAA results will tell you that most of these questions begin with one of the above words (or how). These cover all different aspects of a product so make sure you include them in your content.
3. Understanding current trends and problems
The results that appear under “People also search for” are subject to vary over time depending on what topics are currently trending on Google. So, you need to generate content that is convincing and can be read for a longer period of time.
How to implement It?
The trick is to strike a healthy balance between information that is too broad for the user to search for and information that is not so common that it ends up on Page 10.
- Update Your Content: This is possible by researching people who have also searched for phrases and then using those phrases as search terms. Avoid being overly specific and instead focus on being broad in your approach. Rather than focusing on a single topic, one approach is to group topics into content clusters.
4. Preventing bounces
If you notice a high bounce rate on your page, it could be because users are unable to find what they are looking for on that page. In that case, even a URL-centric People also search for results may be unable to assist them in locating what they require.
How to implement It?
It is not sufficient to merely expand upon the content that is already on your website. The primary objective is to give it an appropriate structure while also concentrating on keywords.
- Google Yourself: You may explore what Google thinks are the most important keywords from your site by looking at the PASF results for your site. Compare this information with the user’s search intent, and you might be able to determine where the issue is coming from.
Tools to find People also search for (PASF) keywords
You do not have to rely on searches that are completely at random in order to discover the keywords that others also search for. Here are some wonderful tools that are capable of doing the same things and even more.
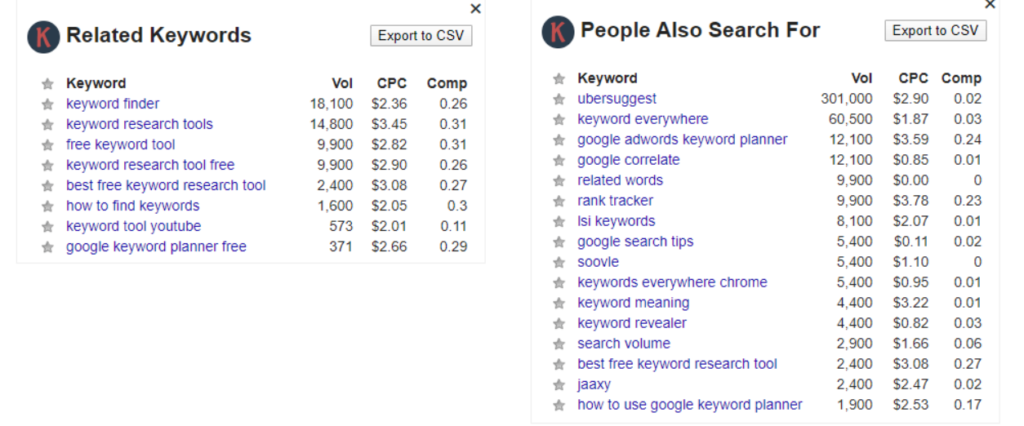
1. Keywords Everywhere
A browser plugin available for both Chrome and Firefox, Keywords Everywhere provides not only PASF keywords but also various other metrics. It functions on the Google search results page itself as appears as two separate boxes on the right.
Feature rundown
- Related keywords and PASF
- Metrics include search volume, CPC, and competitiveness
- Data can be exported as a CSV
- Can save specific keywords, including adding all keywords from a page onto a list
- Works on individual web pages and not just Google search results
- Can offer country-wise metrics
- Historical trend data for 2 sites – Google and YouTube
How to use it?
- Install the extension for Chrome or Firefox.
- Once done, Keywords Everywhere will automatically appear on your search pages.
- The Keywords Everywhere icon on the top right offers a dashboard for analyzing individual page content or adding keywords onto a list.
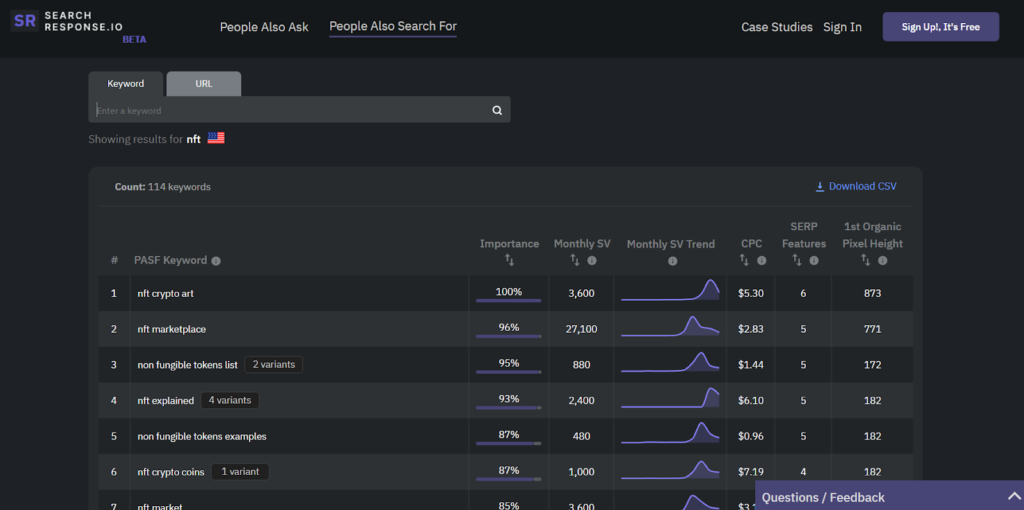
2. Search Response
Search Response offers both an online PAA and PASF tool. The latter is here known as the PASF tool (People Also Search for Keywords). Currently, the tool is free to use as it is still being tested and is in its BETA version.
Feature rundown
- Both PAA and PASK tool
- Look at monthly search trends, search volume, keyword importance, CPC, and SERP Features.
- Also look at 1st Organic Pixel Height which shows how low the 1st organic result is on a results page.
- Filtering of data and country-wise data offered
How to use it?
- Visit the Search Response website.
- Select either the PAA or PASF tool depending on your need.
- You can conduct searches using both keywords and URLs so select one among the two.
- Select the region you want to get insights from.
- Enter the data and that’s it!
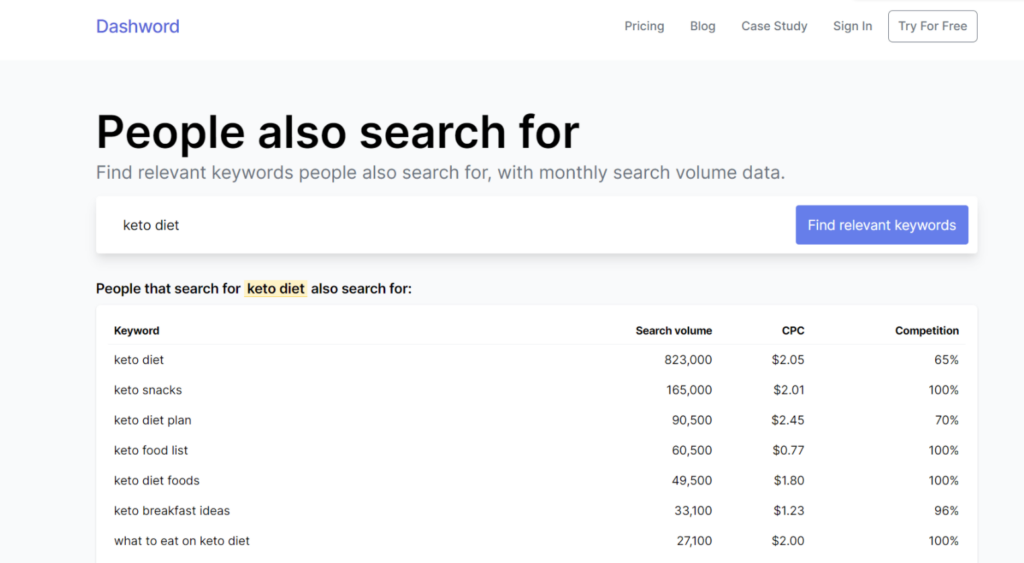
3. Dashword
Along with their many other SEO tools, Dahsword also offers a PASF finder. Dashboard’s PASF Finder is free, and as such, it offers limited features. However, it is still a reliable PASF finder for Google.
Feature rundown
- Offers PASF keywords based on Google recommendations
- Shows search volume, keyword difficulty, and CPC for the keywords
- Free to use but no exporting option is available.
How to use it?
- Visit the Dashword PASF Finder page.
- Enter the keyword you want information on and press enter
- Voila! A list is generated.
4. Answer the Public
With a unique data visualization style, Answer the Public offers Google search insights for absolutely free. The results are displayed as branches from primary to secondary to tertiary levels which makes it great for identifying parent keywords. It is worth noting that Answer the Public uses Google autocomplete to find their results.
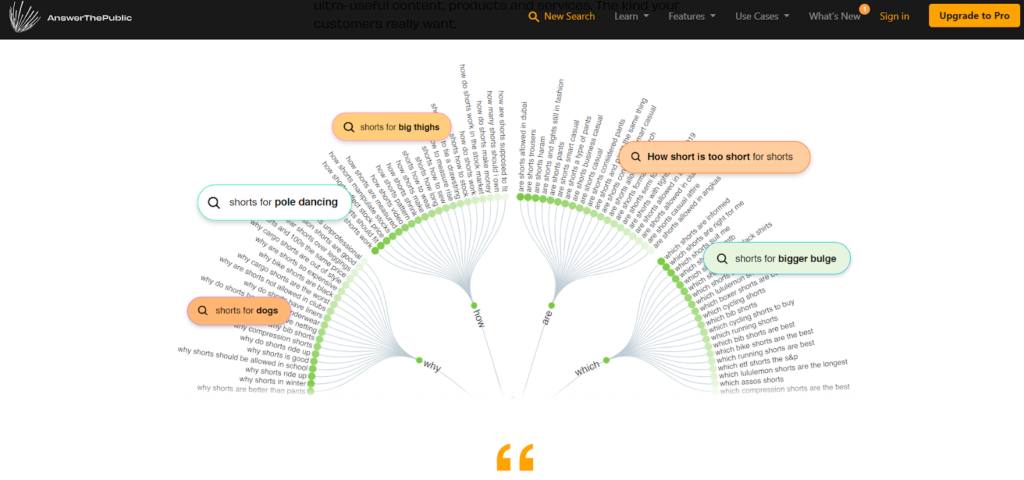
Feature rundown
- Data is shown both as visualization and as text.
- Look at the 5W’s and H previously discussed
- Alphabetical, preposition-wise, and question-wise arrangement of data
- Can export data as CSV file and save images onto the system
How to use it?
- Visit the Answer the Public website.
- Enter the keyword in the space provided
- Enter the country you want to get data from
- Observe the results as they appear in the form of a branch
- Export the data in the form of a CSV file
- With the Pro version, you can compare multiple keyword results
How to rank in Google People also search for (PASF) box?
To appear in the Google People also search for section, optimize your content in the same way you would for any other keyword. This involves paying attention to the searcher’s query in a clear and relevant manner and using appropriate HTML headings to direct Google to the relevant sections of your content.
You can improve your chances of ranking for the People also search for box by implementing the following procedure.
1. Determine and use key search terms
To increase your chances of ranking well for a particular keyword, try using one of the above mentioned tools to identify long-tail keywords that may be more attainable for your website to rank for. Conduct extensive keyword research to identify relevant search terms for your content. Incorporate related search terms and popular search engine questions to boost the ranking of your website.
2. Correct search intent
To determine the purpose or goal of a search, it is crucial to understand the search intent for a specific keyword. This can be done by searching for the keyword on Google and examining the top ranking results.
Paying attention to what Google considers relevant for that keyword. It can help you create a related blog post. You should not overlook this step as it is a key factor in ranking.
3. Make an excellent outline
To create a content outline, it’s helpful to start by identifying a primary topic and then brainstorming related topics. This will enable you to produce valuable content that caters to your target audience’s search intent and helps you become an expert in your industry.
By offering valuable information, you can increase the chances of being found in organic search results and establish yourself as a reliable source of information. This can be an effective way to attract potential customers and drive business growth.
4. Interlinking blog posts
To ensure that your website is optimized and effective, it is important to create connections between your pages, known as “interlinking.” This involves adding links from one page on your site to related pages on the same site. This helps to create a comprehensive network of information and demonstrates to search engines that you have a strong understanding of your topic.
It is recommended to have at least three links pointing to a page from other articles on your website. Interlinking is similar to obtaining backlinks, but from within your own site.
5. Include FAQ schema on your web pages and blog posts
By adding a FAQ schema to your website, you can optimize your pages and take advantage of Google’s search assisted features. This specialized markup code optimizes your content making it eligible for rich snippets on Google SERPs.
To get in People also search for and get Rank 0 on search engine results page (SERP), you can try the above steps.
Please note that it may take a few months to see improvement. If you are not seeing improvement in your ranking after a few months, it is possible that you are targeting a competitive keyword that requires backlinks in order to rank higher.
Backlinks
Links from external websites to your own website are known as backlinks. These links are important for search engine ranking because they demonstrate that your content is trustworthy and credible.
Closing Thoughts
On the whole, a lot revolves around creating the right type of content. People also search for keywords can help you find the right kind of keyword variations to add to your content that will fulfill users intent. But structuring them, making them SEO and user friendly completely depends on your objectives.
Google “People also search for” keywords are great for creating actionable content. You can understand more on how to engage users on your website or get that long click thing going.
This article hopefully gave you better understanding and insights into what “People also search for” box is and how it works to your SEO, PPC and content marketing advantage.